A blown starter fuse can cause big problems, like a car that won’t start. The starter relay is key, controlling the starter motor and solenoid circuit. It acts as a high-current switch, giving power to start the engine. If the starter fuse blows, this connection is lost, making it impossible to crank the engine.
Other signs of a blown starter fuse include clicking sounds and the starter not working right. These issues show there’s an electrical problem that needs fixing fast. This is to avoid more problems and breakdowns.
Key Takeaways
- A blown starter fuse can cause the car to not start at all, leading to sudden breakdowns.
- Common symptoms include clicking sounds, occasional starting failures, and the starter not disengaging properly.
- Electrical issues like a blown fuse, wiring problems, or starter malfunctions can all contribute to these starting system problems.
- Seeking professional diagnosis and repair is crucial for addressing starter fuse-related issues effectively.
- Regular maintenance and fuse inspections can help prevent future starter fuse blowouts.
Understanding the Starter Fuse
The starter fuse is key in a vehicle’s electrical system. It protects the starter motor and circuits from too much electricity. This fuse is a safety net, stopping damage to the starter and other parts. You can find it in the fuse box, either under the hood or inside the car.
It controls the high current needed to start the engine. This ensures the starter motor gets enough power without harming other electrical systems.
What is a Starter Fuse?
A starter fuse is a small device that stops electric current if it gets too high. It prevents damage to the starter motor or other parts from electrical shorts or overloads. These fuses usually handle 10-15 amps, depending on the vehicle’s needs.
Importance of a Starter Fuse
The starter fuse is crucial for the vehicle’s electrical system to work right. It guards the starter motor, wiring, and other parts from damage. This includes problems like starter circuit issues, fusible link melting, or starter relay failure.
By cutting off current when needed, the fuse keeps the system safe and reliable. This reduces the chance of fires, component failures, and other issues.
Common Applications of Starter Fuses
Starter fuses are used in many vehicles, like cars, trucks, SUVs, and motorcycles. They’re a key part of the starting system, protecting against electrical overloads and short circuits. You can find the starter fuse in the fuse box, close to the starter motor or battery.
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Typical Starter Fuse Rating | 10-15 amps |
| Starter Relay Lifespan | 50,000 to 100,000 km (4 to 8 years) |
| Average Starter Relay Replacement Cost | $55 to $80 (parts: $20, labor: $25 to $60) |
Symptoms of a Blown Starter Fuse
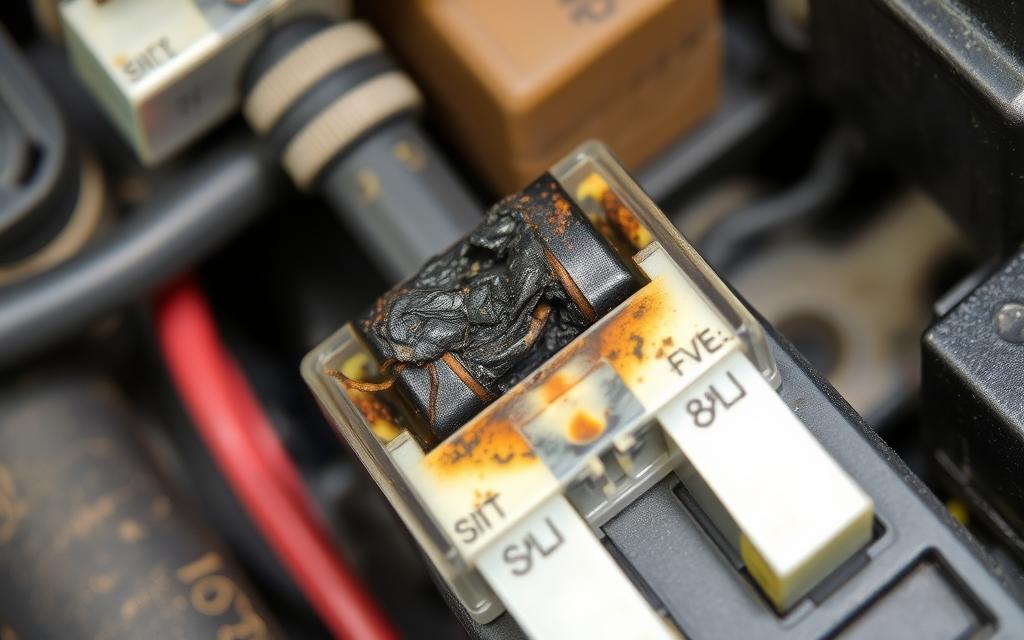

A blown starter fuse can cause several concerning symptoms. These signs may seem unrelated at first. It’s important to spot them early for quick diagnosis and fixing.
Engine Won’t Turn Over
One clear sign of a blown starter fuse is when the engine won’t start. When you turn the ignition, you might hear nothing. This suggests a problem with the starter motor, not just a dead battery.
Electrical Systems Malfunction
A blown starter fuse can also mess with your car’s electrical systems. The dashboard lights might not turn on, and things like the radio or power windows could stop working. This is a strong hint that the starter fuse needs fixing.
Unusual Clicking Sounds
Trying to start a car with a blown starter fuse might make odd clicking sounds. These clicks mean the starter relay is trying to work, but it can’t because of the fuse. This noise is a clear sign of a blown fuse, not just another electrical problem.
Spotting these symptoms of a blown starter fuse is key to quick fixes. Ignoring them can damage your car’s electrical parts and leave you stuck on the road.
Diagnosing Starter Fuse Issues

When you face starter fuse problems, it’s important to be thorough. First, check the fuse visually. Look for melting, discoloration, or a broken metal strip. These signs mean the fuse has blown.
If the fuse looks fine, use a multimeter to check the voltage at the fuse terminals.
Visual Inspection of the Fuse
Examine the starter fuse for any damage. A blown fuse will show signs like overheating or a broken metal strip. If it looks good, then check the voltage next.
Checking Voltage with a Multimeter
Measure the voltage at the fuse terminals with a multimeter. If everything’s working, you should see about 12 volts. A reading of 0 volts or much lower means there’s a problem.
Consulting the Vehicle Manual
Look in the vehicle’s owner’s manual for the starter circuit fuse. It will tell you the fuse rating and where it is. This info is key for fixing the fuse right.
Some cars have a relay and a solenoid in the ignition. Make sure you know which one to check. If the fuse looks good but the problem stays, you might need to look at the relay or solenoid.
By following these steps, you can find and fix starter fuse problems. Fixing these issues quickly can save you from bigger and more expensive repairs. This is true for ignition switch and starter circuit problems too.
Consequences of Ignoring Blown Fuse Symptoms

Ignoring a blown starter fuse can harm your car’s electrical system and safety. Trying to start the car with a blown fuse can damage the starter motor and other important parts. This can lead to big problems.
Potential Damage to Electrical Components
A blown fuse can cause short circuits, leading to heat. This heat can melt or damage metal parts. This might mean you’ll have to replace the starter or other parts, which is expensive.
Increased Repair Costs
Not fixing a blown fuse can make the problem worse. This can lead to more costly repairs. Fixing it quickly can prevent more damage and save money.
Safety Risks on the Road
A car with a blown fuse might not start or could fail while driving. This is dangerous for everyone on the road. It’s important to keep the fuse working right for safety.
Fixing a blown fuse quickly is key to avoiding these issues. Ignoring it can cause more electrical problems. This makes repairs more expensive and complicated.
Common Causes of a Blown Starter Fuse
If your car’s starter fuse keeps blowing, you need to find out why. Blown fuses often mean electrical problems, old wiring, or a bad starter motor. Knowing these reasons can help fix the issue and keep your car’s electrical system working well.
Electrical Short Circuits
Electrical short circuits are a big reason for blown starter fuses. This can happen when wires get damaged or exposed. A short circuit can cause too much current, blowing the fuse. Checking your wiring regularly and fixing any damage can help avoid this.
Old or Worn Wiring
Wiring in your car’s electrical system can get old and worn out. This can lead to short circuits or too much current. When insulation wears off, it can let current leak or cause shorts, blowing the fuse. Replacing old wiring can stop this problem and keep your starter system working right.
Faulty Starter Motor
A bad starter motor can also blow your fuse. If the starter uses too much current, it can overload the fuse. This might be because of a failing solenoid or worn brushes. Replacing the starter motor might be needed to fix this and stop fuse problems from happening again.
Finding out why your starter fuse keeps blowing is key to fixing it for good. By fixing electrical shorts, replacing old wiring, and fixing starter motor issues, you can make sure your car starts up smoothly and reliably.
| Cause | Explanation | Preventative Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Short Circuits | Damaged insulation or exposed wires in the starter circuit can cause a sudden current surge, overloading the fuse. | Regularly inspect wiring and address any signs of wear or damage. |
| Old or Worn Wiring | Deteriorating insulation on wires can lead to current leaks or short circuits, causing the fuse to blow. | Replace old or damaged wiring to maintain the integrity of the electrical system. |
| Faulty Starter Motor | A malfunctioning starter motor that draws excessive current can overload and blow the fuse. | Diagnose and replace the starter motor if it is the root cause of the problem. |
By knowing why starter fuses blow, you can take steps to fix the problem. This ensures your car’s electrical system works well and avoids future issues.
How to Replace a Blown Starter Fuse

If your car’s starter fuse has blown, you need to fix it fast. This is to prevent more electrical problems or safety risks. Replacing a blown starter fuse is easy with just a few tools.
Tools Required for Replacement
- Fuse puller or small pliers
- Replacement fuse of the same amperage rating
- Multimeter (optional, for testing the fuse and electrical system)
Step-by-Step Replacement Guide
Here’s how to replace a blown starter fuse:
- Find the fuse box in your car, usually in the engine area or under the dashboard.
- Check your car’s manual to find the right fuse for the starter circuit.
- Use a fuse puller or small pliers to remove the old fuse. Look for damage, like a melted fusible link, which is a sign of a starter fuse blown symptoms.
- Put in the new fuse, making sure it’s the same amperage as the old one.
- Close the fuse box cover and test the car’s starter to see if the problem is fixed.
If the new fuse blows right away, there might be a bigger electrical problem. It’s wise to get a professional mechanic to find and fix the fusible link melted issue.
Replacing a blown starter fuse is simple. But, make sure the new fuse is the right amperage and there are no other electrical problems. Fixing it quickly helps avoid damage to your car’s electrical parts and keeps it running safely and reliably.
Preventative Measures for Starter Fuse Issues

Keeping your vehicle’s electrical system in good shape is key to avoiding starter fuse problems. Regular checks are vital to spot and fix issues early. Think about using better fuses and protecting wiring from damage.
Regular Maintenance Checks
Check your vehicle’s electrical system often, including the battery, alternator, and starter motor. Testing the electrical system twice a year can catch problems before they cause a blown fuse. Also, test the battery voltage monthly and keep the terminals clean and tight.
Upgrading to High-Quality Fuses
Using top-notch fuses can lower the chance of fuse failures. These fuses handle electrical surges better, protecting your starter circuit and other important parts.
Protecting Wiring from Damage
Make sure wiring is well-secured and safe from heat, moisture, or moving parts. Regularly check wiring for wear or damage. Fix any problems quickly to keep your electrical system working right.
By taking these steps, you can prevent starter circuit problems, electrical issues, and wiring faults. This reduces the chance of a blown starter fuse and keeps your vehicle running smoothly.
| Maintenance Recommendation | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Electrical system load testing | At least twice a year |
| Battery voltage testing | Monthly |
| Battery terminal cleaning | Regularly, during oil services |
| Wiring and connector inspection | During regular maintenance |
“Proper maintenance of the electrical system is crucial to prevent costly repairs and ensure the reliable operation of your vehicle.”
When to Seek Professional Help
If replacing the starter fuse doesn’t fix the issue, it’s time to get help from a pro. Some signs show you need expert help with starter fuse problems.
Signs That Require Expert Attention
- Intermittent starting issues: If your car starts and stops, it might have a bigger electrical problem. A pro can figure out what’s wrong.
- Unusual noises when starting: Clicking, grinding, or whirring sounds mean something’s wrong with the starter or other parts.
- Visible damage to electrical components: Burnt wires or a charred fuse box need a mechanic’s check.
Finding a Qualified Mechanic
Finding a good mechanic for starter fuse and electrical issues is key. Look for a shop or dealership with experts in car electrical systems. They should know how to fix starter and ignition switch problems, and other electrical issues.
Cost Considerations for Repairs
Fixing starter failure or ignition switch problems can cost a lot. It depends on the problem and your car’s model. You’ll pay for diagnosis, parts, and labor. Simple fixes might be cheap, but complex problems cost more. Talk about the cost with your mechanic before they start work.
Knowing when to get expert help and finding a good mechanic is important. It ensures your car’s electrical system is fixed right. This helps avoid more damage and keeps your car safe and running well.
Difference Between Blown Fuses and Other Issues

When your car won’t start, finding the real problem is key. A blown fuse might be the cause, but other issues like no crank no start, dead battery, or starter relay failure can look similar. Knowing the difference helps fix the problem right.
Starter Motor Failures
If your starter motor is broken, you might hear grinding or nothing at all when you turn the key. This means the starter itself is the problem, not just a fuse. You’ll need to fix or replace the starter, not just the fuse.
Battery Problems
A dead battery can make your car crank slowly or lights dim. It might seem like a fuse issue, but it’s really about the battery’s power. Fixing the battery is the right move.
Ignition Switch Malfunctions
Problems starting or electrical issues while driving could mean a bad ignition switch. This part is vital to the car’s electrical system. If it fails, it can seem like a fuse problem. You’ll need to replace the ignition switch to fix it.
These issues might seem like a blown fuse at first, but they need different fixes. Getting the right diagnosis is important to avoid wasting time and money. By understanding these differences, you can fix your car’s problem effectively.
How to Test a Starter Fuse
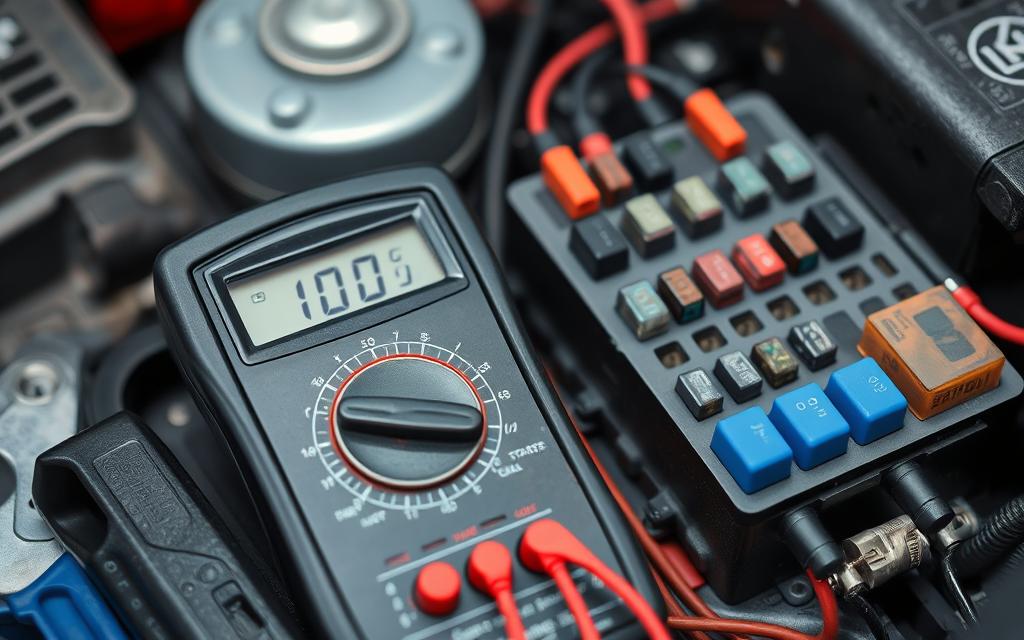

If you think your car’s starter fuse has blown, you need to check it fast. A bad starter fuse can cause many electrical problems. This includes the engine not starting and other electrical issues. Knowing how to test a starter fuse helps you find and fix problems quickly.
Using a Test Light
Testing a starter fuse with a test light is easy. First, connect one end of the test light to a metal part of the car. Then, touch the other end to each side of the fuse. If the light shines on both sides, the fuse is good.
If the light doesn’t shine on one or both sides, the fuse is blown. You’ll need to replace it.
Multimeter Testing Techniques
For a more detailed check, use a multimeter. Set it to the continuity or resistance setting. Touch the probes to the fuse’s ends.
If the multimeter shows a reading close to zero ohms, the fuse is working. But, if it shows a high resistance or no reading, the fuse is blown.
Interpreting Test Results
Remember, a fuse might look fine but still be bad. If your tests show a blown fuse, even if it looks okay, replace it. This ensures your car’s electrical system works right.
By knowing how to test a starter fuse, you can quickly find and fix problems. This keeps your car’s electrical system running smoothly.
| Test Method | Good Fuse Indication | Blown Fuse Indication |
|---|---|---|
| Test Light | Light illuminates on both ends | Light fails to illuminate on one or both ends |
| Multimeter (Continuity) | Reading close to 0 ohms | No continuity or high resistance reading |
The Role of Fuses in Vehicle Safety

Fuses are key to keeping your car safe. They prevent big electrical problems. These small parts protect your car’s electrical systems from short circuits and power surges.
Preventing Electrical Fires
Fuses help keep your car safe from electrical fires. They stop the flow of electricity when there’s too much or a short. This stops wiring or parts from overheating and catching fire.
Protecting Critical Components
Fuses also protect your car’s important parts. This includes the starter motor, alternator, and electronic control units. They keep these parts safe from damage from starter circuit problems or wiring faults.
Enhancing Vehicle Longevity
Fuses help your car last longer. They keep electrical systems safe from damage. This means your car works better and longer, saving you money on repairs.
In short, fuses are heroes for your car’s safety. They stop fires, protect important parts, and make your car last longer. Knowing their value helps you appreciate their role in keeping you safe on the road.
Understanding Fuse Ratings and Specifications
Fuses are key in vehicle electrical systems, protecting parts from electrical problems. They come in types like blade, glass tube, and fusible links. Starter fuses have higher amperage ratings to handle the starter motor’s high current.
Types of Fuses Used in Vehicles
Most cars have two fuse boxes, one in the engine and another under the dashboard. These fuses vary in shape, color, and size, mostly being rectangular or cylinder-shaped.
Common Ratings for Starter Fuses
Starter fuses usually range from 30 to 80 amps. This range depends on the vehicle’s make and model. The high ratings meet the starter motor’s power needs during engine start-up.
Choosing the Right Fuse for Your Vehicle
Choosing the right fuse is vital. Always use a fuse with the same amperage as the blown one. A higher-rated fuse can damage the system, while a lower one might blow again, causing starter circuit problems and electrical issues. Check your owner’s manual for the correct fuse for your car.
| Fuse Type | Typical Rating Range | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Blade Fuse | 5-80 amps | Lighting, accessories, small motors |
| Glass Tube Fuse | 30-100 amps | Starter, alternator, high-power accessories |
| Fusible Link | 50-200 amps | Battery, alternator, high-current circuits |
Choosing and maintaining the right fuse is key. It prevents fusible link melted problems and keeps your vehicle’s electrical system running smoothly.
Warning Signs of Related Electrical Problems
It’s key to know the signs of electrical troubles in your car. Look out for flickering dashboard lights or unresponsive accessories. These signs can point to bigger issues.
Flickering Dashboard Lights
Flickering or dim dashboard lights might mean alternator problems or loose wires. This could show the alternator isn’t charging the battery right. Or, there might be a wiring issue. Fixing these problems fast can stop bigger electrical issues or even starter failure.
Inconsistent Power Supply
Dimming lights or flickering accessories suggest a power problem. This could be from wiring faults or a failing battery or alternator. Watching your car’s electrical behavior can help find the problem early.
Unresponsive Accessories
When your car’s extras, like power windows or the radio, don’t work, it’s a sign of a bigger issue. This could be a bad fuse, wiring problem, or a faulty electrical part. Fixing these issues quickly can prevent more damage and keep your car’s electrical systems working right.
By watching for these warning signs, you can fix problems before they get worse. Regular car checks and quick action to electrical oddities can keep your vehicle running well.
An Overview of Vehicle Electrical Systems
Vehicle electrical systems are key to modern cars, powering important parts for safe and efficient driving. The battery is at the center, storing and giving out electricity. The alternator then charges the battery and powers the car’s electrical circuits.
Key Components of Electrical Systems
The main parts of a car’s electrical system are the battery, alternator, starter motor, and control modules. Fuses are also crucial, protecting circuits from damage and short circuits.
How Fuses Fit Into the System
Fuses are placed between the power source and the circuits they protect. They cut off electricity when a circuit draws too much current. This prevents damage and fire risks.
Importance of Proper Functioning of the System
A car’s electrical system must work right for it to run well and safely. It’s key for starting the engine and powering safety features. Fixing starter circuit problems, ignition switch problems, and electrical issues is vital for smooth driving.
Regular checks on the battery, alternator, and fuse box can stop many electrical problems. This keeps the car’s electrical system healthy for a long time.
“A well-maintained electrical system is the foundation for a vehicle’s reliable performance and safety.”
Conclusion: Staying Alert to Signs of a Blown Starter Fuse
It’s important to watch for signs of a blown starter fuse to keep your car safe and running well. Look out for the engine not starting, electrical system problems, and strange noises. Fixing these issues quickly can save you from bigger problems and expensive repairs later.
Summary of Key Points
In this article, we’ve covered the starter fuse’s role, common symptoms of a blown fuse, and how to fix them. We found that 15% of drivers see dim cabin lights when starting their car, hinting at starter motor trouble. Also, 20% of starter faults make clicking or whirring sounds, and 10% keep spinning after the engine starts.
Importance of Timely Action
Acting fast when a starter fuse blows is key. Ignoring it can harm your car’s electrical parts and cost more to fix. Sometimes, a blown fuse can even be dangerous on the road. Knowing why fuses blow, like short circuits or old wiring, helps you avoid and fix these problems.
Encouragement to Maintain Vehicle Health
Keeping your car’s electrical system in good shape is vital for its performance and life. Regular checks, using quality fuses, and protecting wiring can prevent fuse issues. By being proactive, you ensure a safer and more reliable drive.
FAQ
What are the common symptoms of a blown starter fuse?
What is a starter fuse and why is it important?
What happens when the starter fuse is blown?
How can I diagnose starter fuse issues?
What are the consequences of ignoring a blown starter fuse?
What are the common causes of a blown starter fuse?
How do I replace a blown starter fuse?
How can I prevent starter fuse issues?
When should I seek professional help for starter fuse problems?
How can I differentiate between a blown fuse and other electrical issues?

Jack Thompson is a writer and seasoned auto mechanic with over 15 years of experience in the automotive industry. Known for his expertise in vehicle mechanics, Jack has a deep understanding of car and truck systems. His skills, honed through years of hands-on experience, have made him a trusted name in the field. Jack is committed to providing valuable insights into car maintenance and repair, helping vehicle owners keep their vehicles in top condition.

